Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account

| Tags |
|---|
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
Richard Platt's insight:
A meta-analysis found that digital health tools promoting physical activity only work for people with higher socioeconomic status. They don’t work for poorer people
Richard Platt's insight:
Wearable tech devices are as popular as ever, especially now that they’re packed with advanced capabilities for tracking sleep data and a slew of biomarkers like Heart Rate Variability/HRV, heart rate, stress, Muscle Ox %, and lactic overload for muscle fatigue. Using this data means establishing your baseline, noting patterns, and getting real-time biometric data that puts the power in your hands for positive changes toward optimized health
Richard Platt's insight:
According to a paywalled report from DigiTimes, Apple and its suppliers have begun working on short-wavelength infrared sensors, a commonly used sensor type for health devices. The new sensors, likely to be fitted on the back of the Apple Watch, will enable the device to measure the amount of sugar in a wearer's blood. According to The Wall Street Journal, however, Apple is facing challenges in incorporating blood glucose capabilities into the Apple Watch. Current methods of measuring blood glucose levels include taking a sample of blood and using a medical-grade device. With the Apple Watch, Apple would be looking to take a typically invasive medical practice and make it non-invasive. The Apple Watch, over the years, has gained more comprehensive health features, most recently with the Apple Watch Series 6 that added a blood oxygen sensor. Compared to the first Apple Watch capable of measuring heart rate and primary daily activity, the Apple Watch is now capable of taking an ECG, detecting falls, high and low heart rates, blood oxygen levels, and more. In iOS 15, the Health app added blood glucose highlights as a health metric. iOS 15 users have to use external hardware to provide the data, but that would change if Apple adds a glucose monitoring feature to a future Apple Watch model.
Richard Platt's insight:
A Penn State research group is confident that the tiny levels of glucose found in sweat can provide a meaningful correlation with the amount found in the blood, and has designed a device to measure sweat glucose levels. The technology involves drawing sweat into a microfluidic chamber, where glucose reacts with an alkaline solution to form a compound that can react with a nickel-gold alloy present in the device. This reaction causes an electrical signal that can indicate the amount of glucose present in the sweat. The device has numerous advantages over another sensor type, that requires enzymes to detect glucose. “An enzymatic sensor has to be kept at a certain temperature and pH, and the enzyme can’t be stored in the long term,” said Huanyu Cheng, a researcher involved in the study, in a press release. “A nonenzymatic glucose sensor, on the other hand, is advantageous in terms of stable performance and glucose sensitivity regardless of these changes.” At only the size of a quarter, the device is unobtrusive. So far, the researchers have tested it with some volunteers and found that it could successfully track changes in blood glucose before and after a meal. “We want to work with physicians and other health care providers to see how we can apply this technology for daily monitoring of a patient,” said Cheng. “This glucose sensor serves as a foundational example to show that we can improve the detection of biomarkers in sweat at extremely low concentrations.”
When you or your kid have any sort of respiratory issue, figuring out what’s happening minute-by-minute — and how well treatment is working — is a stressful, frustrating, and anxiety-filled process. I imagine it’s all of the above and more in the middle of a friggin’ RESPIRATORY DISEASE pandemic. StethoMe, a team competing in this […]
Richard Platt's insight:
When you or your kid have any sort of respiratory issue, figuring out what’s happening minute-by-minute — and how well treatment is working — is a stressful, frustrating, and anxiety-filled process. I imagine it’s all of the above and more in the middle of a respiratory disease pandemic. StethoMe, a team competing in this week’s TechCrunch Disrupt Startup Battlefield competition, is looking to help alleviate some of this for children with asthma and their parents. It has built a smart, connected stethoscope that can help parents perform lung examinations at home, sending high-fidelity recordings directly to their doctor and using ML to help flag potential concerns. Using your phone to tell it what kind of exam you want to perform, and the built-in screen will walk you through the process. It’ll tell you where on the chest to place the device, whether or not the room you’re in is quiet enough, and more. After measuring across 6-8 points, it’ll provide you a report with details like respiratory rate, heart rate, and whether or not it detected any audio abnormalities — including wheezing, rhonci (gurgling sounds caused by fluid), or crackles. From there, you’re able to send a link to the report directly to your kid’s doctor, where they can hear the recorded audio from each point on the chest. A scrubbable spectrogram, meanwhile, provides a visual overview of each recording and flags and labels any abnormalities detected by the system. StethoMe says it has raised a few rounds at this point (a $400K pre-seed, $2M seed, and $2.5M Series A) and received nearly $3M in grants from Poland’s National Center for Research and Development.
Richard Platt's insight:
Apps that fail to disclose incidents can be fined over $43,000 per violation per day.
Richard Platt's insight:
Ray-Ban Stories, start at $299 and come in 3 styles, including the iconic Ray-Ban Wayfarer, and 5 hues. Initially, they're being sold at some Ray-Ban stores and at Ray-Ban.com, but what will become of you if you buy them - Was this accidentally furtive photo- and video-taking turning me into a Facehole? - Even while pushing a computer that sits on your face and looks quite similar to regular glasses, Facebook and Ray-Ban are emphasizing the importance of making other people aware that you may be recording them. The glasses can only take videos up to 30 seconds long, and the LED on the front of the glasses is meant to be visible from 25 feet away; it shines the whole time you're taking a video. And after days of trying them out, I still didn't have the sense that I (or anyone, really) needs Ray-Ban Stories. You may need eyeglasses or sunglasses, and a smartphone, too. But it's going to be tough for Facebook to convince most people that they have to have a gadget that can replicate a few of their phone's features while sitting on their face — even one that looks this good. You can turn on FB Assistant through the View app to use voice commands for taking photos and videos — a way to make it painfully obvious that you're capturing the world around you — but not for anything else, like controlling music playback. Despite these efforts, I couldn't shake the feeling that I was getting away with something while wearing Ray-Ban Stories in public. As far as I could tell, nobody noticed anything unusual about the glasses while chasing my kids around a busy playground, even when I was taking numerous short videos. (It was impossible for me to tell, but perhaps the bright sunlight made the glasses' white LED less noticeable.) I walked into stores with them on, took pictures of myself in mirrors, and nobody even blinked. It would have been easy to use these glasses to invade other people's privacy.
Apple wants to add more advanced health features to the Apple Watch, but we're skeptical they'll arrive this year.
Richard Platt's insight:
While a number of new health features are reportedly in the works at Apple on its new watch, the two big ones are blood pressure-tracking and a thermometer to help with fertility planning. Both features already exist on wrist-based wearables, albeit not in as sleek a package as the Apple Watch. Omron made the 1st FDA-cleared blood pressure smartwatch (2019), with an inflatable strap. Samsung also has a blood pressure feature for its smartwatches, though it’s not available in the U.S. for regulatory reasons, and requires you to calibrate using a more traditional blood pressure-measuring device. Ava is a fertility tracker that measures not only body temperature but also things like perfusion to help couples trying to conceive. Fitbit also added a body temperature sensor to its Sense smartwatch, and the Oura Ring has had one for ages. According to a WSJ report, Apple’s blood pressure feature would attempt to show users how their blood pressure was trending without the need for baseline systolic and diastolic measurements. (This is why Samsung needs calibration for its blood pressure feature.) Current smartwatch sensors can’t really do this, unless they can be improved. Apple is trying to approximate traditional blood pressure calibration devices by measuring the “speed of the wave a heartbeat sends through a person’s arteries.” and is reportedly exploring the ability to take readings without an inflatable cuff at all. It’s not groundbreaking that Apple is exploring these health features—everybody is doing it and has been for years. Aside from when it added FDA-cleared ECG sensors to the Series 4, Apple isn’t known for being the first to any particular health feature. Detailed sleep tracking, SpO2 sensors, and cardio fitness metrics have been around way before Apple added them to the Series 6 and watchOS 7. The point is Apple generally doesn’t tip its hand until it’s 100% sure what it’s got is good, or at least sufficient to meet its high standards. This would be a big deal if the company could pull it off in a design similar to the current Apple Watch.
Smartwatch shipments grew by a whopping 47 percent in Q2 thanks to more demand for health tracking — and it wasn't just Apple and Samsung enjoying success..
Richard Platt's insight:
Strategy Analytics estimates smartwatch shipments grew by a whopping 47% Y-o-Y in Q2 of 2021, with 18.1 million of the wearables shipping this spring. Demand (at least from retailers) has returned to "pre-pandemic levels," according to the analyst firm's Steven Waltzer — it hasn't been this hot since 2018. Strategy Analytics attributed the spike to continued demand for personal health devices. It's not clear how much the pandemic recovery fuelled demand, although it wouldn't be surprising if the renewed interest in going outside prompted extra sales. It wasn't just the usual companies that benefited from the surge; Apple held on to a comfortable lead with 52% of the market, and Samsung saw its shipments jump 54%. Garmin's fitness-focused watches still jumped 25%, though, and "others" (including Fossil and other Wear OS backers) saw their shipments climb 55%. This was a strong overall market, even for smaller brands. There are signs this spike will continue. Apple Watch Series 7 could be weeks away as we write this, and Samsung's Wear OS-packing Galaxy Watch 4 might revitalize Android smartwatch sales. Low-cost LTE smartwatches from Chinese brands like Oppo and Xiaomi might also help, according to the analysts. This momentum will eventually die down, but it's unlikely to fade in the near future.
Richard Platt's insight:
Wear OS smartwatches over the last couple of years, have been over-promised on functionality by Qualcomm's processors. The Wear 4100 was mislabeled as something of a savior, going down to 12nm from the 28nm EUV process on which the Wear 3100 was built. Alas, it wasn't that much of an improvement, and Wear OS continues to perform pretty badly. With any luck, Samsung's new 5nm processor will be just the kick up the backside Wear OS needs. The freshly announced Exynos W920, which is set to debut in Samsung's upcoming Galaxy Watch4 series, promises 20% better CPU performance and 10x the GPU performance of its predecessor. This is thanks to 2 high-performance Arm Cortex-A55 cores and an Arm Mali G68 GPU, which can support up to a qHD display (969x540). And all of this comes in the smallest available wearables chipset, with LPDDR4 RAM and eMMC storage on board. As well as allowing for smaller hardware with bigger batteries, the new silicon includes a dedicated low-power display processor (Cortex-M55) that allows for Always-on-display functionality with minimal detriment to battery life. Other features include a 4G LTE Cat.4 modem and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) L1 for activity tracking. The Exynos W920 will launch with Samsung's Galaxy Watch4 series, alongside the companies next-generation of foldable phones — it all gets unveiled tomorrow. The smartwatches will be the first to run the Samsung/Google co-developed version of Wear OS, which we're pretty excited about.
Flexible electronics have been done before, but not on this scale.
Richard Platt's insight:
Wearable electronics, like watches and fitness trackers, represent the next logical step in computing. They've sparked an interest in the development of flexible electronics, which could expand the category to include products like clothing and backpacks. Flexible electronics run into a problem, however: Our processing hardware is anything but flexible. Most efforts to deal with that limitation have involved splitting up processors into a collection of smaller units, linking them with flexible wiring, and then embedding all the components in a flexible polymer. To an extent, the process is a throwback to the early days of computing, when a floating-point unit might reside on a separate chip. But a group within the semiconductor company Arm has now managed to implement one of the company's smaller embedded designs using flexible silicon. The design works and executes all the instructions you'd expect from it, but it also illustrates the compromises we have to make to produce truly flexible electronics. Not quite CMOS - The basic idea behind flexible electronics is remarkably simple: start with a flexible substrate (like plastic or paper) and use it as a substrate for fabricating a thin layer of a flexible semiconductor. A variety of semiconductors fit the bill, ranging from atomically thin materials to semiconducting polymers. But most of the options aren't mature technologies with respect to their use in the fabrication of logic gates, so working with them involves two layers of experimentation—both with the materials themselves and with their flexibility. Amorphous silicon is a somewhat familiar option. The silicon used in the manufacture of existing processors is crystalline, meaning it's in the form of an ordered array of atoms. Amorphous silicon isn't, and it's flexible as a result. Plus, we know how to work with amorphous silicon, since we use it for things like solar panels and LCDs. It's also inexpensive, partly because it can be processed into transistors through simpler techniques than needed for crystalline silicon. The downside is that amorphous silicon comes up short in several measures, including performance, power efficiency, and circuit density. That said, many of the potential uses for flexible electronics don't require much in the way of performance. PlasticArm - In keeping with the idea of minimal performance requirements, the team at Arm worked with PragmatIC Semiconductor to implement a version of Arm's Cortex M0+ processor termed "PlasticArm." The M0+ is a 32-bit processor that can execute a simplified subset of the Arm "thumb" instructions; it's optimized for small sizes and low power use, and it is generally used as an embedded processor. Even by the standards of a very simplified processor, PlasticArm had some distinct features that set it apart. For one thing, the small bits of memory that processors use to store the data they're working on (called "registers") are normally located in the processor itself because it kills performance to go to external RAM in order to read this memory. To simplify the PlasticArm's processor, the CPU's registers are located in a reserve section of the RAM—and the system was made with only 128 bytes of RAM. The system and applications that run on PlasticArm are held in a 456 byte ROM chip that is also separated from the processing hardware. Right now, the ROM can't be updated (it's read-only), but the team hopes to change that in the next iteration. All the key pieces—the processor, the RAM, the ROM, and the interconnects—were made using amorphous silicon and fabricated on a flexible polymer. The system also has pins for off-chip communications. Overall, the performance isn't good. Its maximum clock speed is a stately 29 kilohertz, and it consumes about 20 milliwatts at that speed. That may sound like very little, but an M0+ implemented on standard silicon only needs a bit over 10 microwatts to hit a megahertz. On the positive side, it has over 18,000 individual gates, which is over an order of magnitude higher than any previously described flexible processor. It also successfully executed all the software in its ROM, although the researchers only did tests without bothering to use the processor's distinctive feature—they never actually flexed it.
Richard Platt's insight:
TCL NXTWear G, a wearable display that puts a 140-inch equivalent screen right in front of your eyes. The NXTWear G have a sunglass-like design, and are fairly lightweight at about 100 grams, so wearing them for the duration of the average movie shouldn’t be a problem. You stare at dual Sony OLED screens each with a Full HD resolution, which gives the impression of looking at a 140-inch, 16:9 aspect ratio screen. TCL says the NXTWear G will show both 3D and 4K resolution video, and because the glasses understand the position of your body, you can watch standing up, sitting down, or laying down and the screen will always stay in front of your eyes.The NXTWear G takes power from the device it’s connected to by a USB Type-C cable. It links to your smartphone, tablet, Windows PC, or Mac’s USB Display Port and effectively mirrors what you’d normally see on the screen. You can watch video from your phone, or make video calls from your computer, for example. Because the NXTWear G doesn’t cover your entire face like a Virtual Reality (VR) headset, you should still see the device, desk, or keyboard to work as normal. TCL says with the glasses connected to a phone — about 100 different models work with the NXTWear G so far — on average the device’s battery should provide enough power to watch about five hours of video. While there are speakers built into the glasses, listening to audio using Bluetooth headphones from the connected device will increase privacy. If you wear glasses normally, there’s the option to add your prescription to a separate lens that magnetically attaches to the inside of the NXTWear G, plus a selection of nose pads are included to help get the best fit. The glasses fold down ready to be stored in a case for easy transportation. TCL has been talking about its wearable display technology for a while, and it was revealed during CES 2021 as Project Archer. We’ve tried prototypes out at trade shows in the past, but we have yet to try it in this new, much more face-friendly hardware design. When will that change? It may be a little while yet, as TCL’s launch plans start in South Korea and Australia in July, with Europe to follow. A North American release is in the plans, but there’s no timeframe yet. |
Richard Platt's insight:
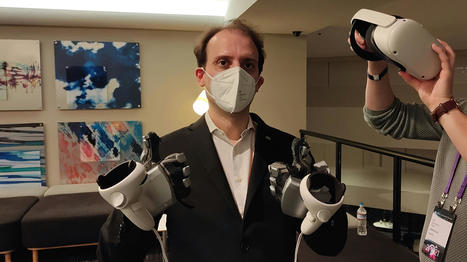
Senseglove Nova is an overall big improvement with regard to the previous version of Senseglove gloves. The only worsening is that the force feedback is slightly weaker, but there have been huge improvements in comfort, usability, design, and tactile feedback. Using these gloves wirelessly has been very cool and I think that with this iteration they are finally usable by every company. The price, $5000, if your company can spare the money but make sure to get good effective and efficient training. Haptics in VR is still in the early stages, so this product is not perfect: the force feedback emulation still needs a lot of work to appear realistic. But when it works well, or where the vibrations on the fingertips are coherent with what you are touching in VR can feel a bit magical, and help you see the potential of this technology, that is the one of increasing the realism of the virtual simulation. The purpose of these gloves (according to the author) is to give decent haptic feedback for an affordable price, and he thinks that it has been fulfilled. If you want perfect haptics, instead, you have probably to wait for more iterations of these devices to start seeing something meaningful for you.
Richard Platt's insight:
HaptX has been working on haptic gloves that employ microfluidic feedback technology, with an aim toward helping enterprise customers working in VR and robotics. In a statement to GeekWire, HaptX founder and CEO Jake Rubin said Meta’s gloves “appear to be substantively identical to HaptX’s patented technology.” Rubin pointed to core components of the Meta prototype, including a silicone-based microfluidic tactile feedback laminate and pneumatic control architecture. In its news release and a longer blog post Tuesday, Meta listed examples of where its team was pushing human-computer interaction forward and “creating new breakthroughs to make haptic gloves a reality.” Among those breakthroughs, Meta listed microfluidics and said it was “developing the world’s first high-speed microfluidic processor.” Rubin said HaptX welcomes “interest and competition in the field of microfluidic haptics; however, competition must be fair for the industry to thrive.” He added that the startup has not heard from Meta but that HaptX would “look forward to working with them to reach a fair and equitable arrangement that addresses our concerns and enables them to incorporate our innovative technology into their future consumer products.” GeekWire has reached out to Meta for reaction to HaptX’s assertions and will update this story when we hear back. Update: Meta declined to respond to HaptX’s assertions.
Richard Platt's insight:
Oura’s Generation 3 smart ring will have a whole new slate of features, including period prediction, blood oxygen monitoring, and real-time heart rate tracking. The new ring will jump from 3 to 7 temperature sensors and add a pulse oxygen sensor, Oura CEO Harpreet Rai told The Verge. A new, green LED light will monitor heart rate throughout the day. Starting at the end of 2021, users will also be able to record their heart rate during exercise and see information about heart rate recovery after a workout is done. The upgrades underscore the company’s focus on health, Rai says, particularly the period prediction feature. The new ring will use shifts in temperature and user feedback to predict when a user might get their period up to 30 days in advance. Body temperature changes through the menstrual cycle, rising just before ovulation and falling as mensuration begins. Oura is also moving to a membership model for its app, priced at $5.99 a month. Users who upgrade from an older ring to the new model will get a discount on the hardware and a free lifetime membership. The Generation 3 ring will start shipping November 15th. Read on for more details.
Supply challenges related to the screen may have delayed the launch.
Richard Platt's insight:
As has become something of a ritual, tools-seller and repair-advocacy group iFixit has published a detailed teardown of the latest Apple product. This time, we get a look at the innards of the Apple Watch Series 7. Of course, iFixit's teardowns are as much about assessing the serviceability of a device as they are about geeking out about hardware changes. iFixit gave the Watch a 6/10 repairability score, citing its "modular construction" and "straightforward access to the screen and battery." Knocks against the Watch include the absence of a service manual and the fact that the screen must be unglued and reglued with every repair. The Apple Watch Series 7 appears to use an on-cell touch OLED panel, the same type seen in the iPhone 13 line. Consulting with a former Apple engineer, iFixit suggests that supply challenges related to this display tech are likely the reason the Apple Watch launched a bit late this year and why the device didn't get a release date in last month's keynote announcing it. Oh yeah the diagnostic port is gone, iFixit speculating Apple now uses a wireless interface to service the Watch and reasonably ventures a guess that this may be a test drive for the eventual removal of the iPhone's lone port. Watch's rated battery life the same as the 2020 model, despite the larger, more power-hungry screen.
Richard Platt's insight:
Withings said it has received clearance from the FDA for its medical-grade ScanWatch, a smartwatch that can detect heart rate problems.
Richard Platt's insight:
With the iOS 15 launch today, some iPhone users will have the option to share data from their Health app directly with their doctors through their electronic medical records. Six health record companies are participating in the initial launch, and some of those companies say that doctors and medical practices on their systems are eager to start using the feature. People will be able to share their Health app data directly into electronic medical records with the launch of iOS 15. It could help doctors keep better track of how patients do outside of office visits. People who use the option can use the new sharing function on the Health app to let their doctor see data like their heart rate and time spent exercising, as collected through the Health app. It could help physicians keep a closer eye on metrics that might be relevant to a patient’s health without the patient having to take an extra step to manually share the information. While the data provided by wearable devices and other health apps can be useful, doctors often say they’re worried about information overload. Joros at Allscripts says the layout of the dashboard within Apple’s health record might help make the flood of information less overwhelming. DrChrono plans to roll the Health app feature to a first set of initial users before expanding gradually to its full customer base, which includes around 4,000 medical practices. The company can track how often the feature is used, and Kivatinos says it plans to collect data on how many patients end up sharing their Health app information into the health record.
Richard Platt's insight:
Xiaomi is challenging Facebook in the wearables arena by launching its own smart glasses. The device won’t only be capable of taking photos, but also of displaying messages and notifications, making calls, providing navigation and translating text in real time in front of your eyes. Like FB, Xiaomi is also putting emphasis on the device’s lightness despite its features. At 51 grams, though, it’s a bit heavier than the social network’s Ray-Ban Stories. In addition, the glasses also has an indicator light that shows when the 5-megapixel camera is in use. Xiaomi’s Smart Glasses are powered by a quad-core ARM processor and runs on Android, using MicroLED imaging technology, having a higher brightness and longer lifespan than OLED. The company says the technology has a simpler structure that enabled it to create a compact display with individual pixels sized at 4μm. You won’t be able to view the images you take in color, though — Xiaomi says it opted to use a monochrome display solution “to allow sufficient light to pass through complicated optical structures.” Its smart glasses won’t be just a 2nd screen for your phone. It’s independently capable of many things, such as selecting the most important notifications to show you, including smart home alarms and messages from important contacts. The device’s navigation capability can display maps and directions in front of your eyes. It can also show you the number of whoever’s currently calling your phone, and you can take the call using the smart glasses’ built in mic and speakers. That mic will be able to pick up speech, as well, which Xiaomi’s proprietary translating algorithm can translate in real time. The glasses’ translation feature also works’ on written text and text on photos captures through its camera. Unfortunately, the company has yet to announce a price or a launch date for the glasses, but we’ll keep you updated when it does.
The global wearable band market grew 5.6% year on year with 40.9 million units shipping in Q2 2021. The decline of basic bands, which started in Q4 2020, has extended into Q2 2021. Shipments fell
Richard Platt's insight:
The global wearable band market grew 5.6% Y-o-Y with 40.9 million units shipping in Q2 2021. The decline of basic bands, which started in Q4 2020, has extended into Q2 2021. Shipments fell 23.8% to 15.5 million units. But the decline of basic bands is being offset by growth in wristwatches. Shipments of basic watches and smartwatches reached 25.4 million, up 37.9%. Wristwatches now account for 62% of global wearable band shipments. Wristwatch shipments overtook those of basic bands for the 1st time in Q4 2020, and this trend has continued since then, with wristwatches accounting for over 60% of all wearable band shipments for 3 consecutive quarters to date. Canalys expects wristwatches to be the key growth driver for the wearable band category for years to come. Xiaomi overtook Apple to become the top-shipping wearable band vendor in Q2 2021. Xiaomi’s performance was bolstered by the launch of the Mi Smart Band 6, despite India, one of Xiaomi’s strongholds, not on the initial global launch list. Huawei hung on to third place, mostly relying on China to stay afloat. “Xiaomi made a wise move to hasten the release of the Mi Band 6, which is a more compelling device than its predecessor,” said Canalys Research Analyst Cynthia Chen. “Xiaomi’s quick pivot to basic watches also helped the company boost its wristwatch shipments by 1.3 million units this quarter.”
Well, well, well, I guess this is what happens when the screen size gets bigger.
Richard Platt's insight:
Until today, it was widely expected that the Apple Watch Series 7 would make its debut at the same time as the iPhone 13 lineup. Now, as Apple’s long-rumored September event approaches, it appears that the Series 7 might be delayed due to production issues. According to Nikkei Asia, the root of the problem is the Series 7's “complicated designs.” Supposedly, small-scale production began last week but the results were unsatisfactory because the design is “significantly different” from previous versions and there were issues assembling electronic modules, components, and displays. The delay was also corroborated by a Bloomberg report, which cited an anonymous source close to the matter. Rumors about the Series 7 have been thin compared to previous years, but one thing that’s been consistent is that the Apple Watch is getting a redesign. So far, we’ve seen some renders of a flat-edged watch that looks like a mini iPhone. Another recent rumor is that the size of screens are increasing, from 40mm and 44mm to 41mm and 45mm. Nikkei claims it’s not necessarily the exterior design causing issues—though the bigger screens ultimately do play a part. The report also says that new features, such as blood pressure monitoring, have required Apple to reconfigure the watch’s internal design. (Blood pressure monitoring is also a fairly new rumor, as it had long been speculated Apple was working on blood glucose monitoring instead.) Or put simply, it needs to cram more components into a watch that’s not that much bigger than its predecessor. This is what’s reportedly causing production issues, a problem that’s only been exacerbated by the pandemic. Specifically, Nikkei says the inability for Apple to work with its suppliers in person to verify specifications means the company is only coming across design challenges once test production starts.
The Galaxy Watch 4 uses a method called bioelectrical impedance analysis to calculate the amount of muscle and fat in someone’s body. It appeared fairly accurate in an initial study.
Richard Platt's insight:
Samsung’s new Galaxy Watch 4 has a feature that can calculate body fat percentage and muscle mass, the company announced yesterday. It’s the latest tech company to offer a body composition feature, joining Amazon, which has a body fat percentage feature in its Halo Band. Body fat is generally a better way to assess health than weight, but it’s often calculated using a metric called the body mass index (BMI), which is crude and inaccurate. If wearables prove accurate, they could give people a better resource to monitor their health, Diana Thomas, a mathematician who studies body weight regulation at West Point, told The Verge. The Galaxy measures body composition using a technique called bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), which sends a weak electric current through the body. It’s calculating the amount of water in the body — the signal moves more quickly through tissue that has higher percentages of water. Since fat has a lower water content than muscle, the technique can estimate how much fat is present in a person’s body. BIA can give an estimate of body fat, but it has limitations, said Thomas. There isn’t a perfect 1-to-1 ratio between the amount of water in the body and body fat, and the amount of water in the body changes over time, she said. It can go up and down with exercise, for example, or if someone is drinking a lot of water. One study found that BIA overestimated body fat if the measurement was taken right after someone drank around two cups of water. Most available devices that use BIA to track body composition send the current through the soles of the feet (like a smart scale) or through the palms. Samsung shrunk the sensors down to fit on the back of the watch. The company’s Healthcare Sensor Lab published a study in January 2021 describing the technology. In the study, 203 people had their body composition analyzed by the watch, two other BIA devices, and a device that uses dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) — an X-ray technique that shows fat distribution through the body, which is considered the gold standard for body composition measurement.
LG's PuriCare Wearable Air Purifier is launching in Thailand in August with improved features including a mic and speaker..
Richard Platt's insight:
With face coverings still the norm, tech companies want you to up your mask game. Last year, LG unveiled the PuriCare Wearable Air Purifier featuring three fans and a pair of HEPA-style filters. 10 months later, it's finally revealed an initial release date for the device, an improved version of which arrives in Thailand in August. There's still no word on the price, however. The latest iteration features a smaller, lighter motor and a built-in mic, speaker and voice amplifier. LG says its "VoiceOn" tech automatically recognizes when you're talking and boosts the sound so others can hear you through the mask. Unfortunately, it can't make you sound like Darth Vader. LG has also bumped up the battery from 820mAh to 1,000 mAh, though the stated 8 hour running time is still the same. It's also touting a two hour recharge time using the included USB cable. The wearable purifier should roll out to more regions upon receiving approval from regulators, the company said. For now, LG is promoting the mask with the help of the Thai Olympics team, who wore it en route to the summer games in Tokyo. Clearly, the Korean company is pitching it as a go-to for those who train outdoors. But, LG's device has its rivals: We've previously seen tech-infused masks from Razer and, um, Will.i.Am.
Richard Platt's insight:
Samsung has taken the wraps off it and Google’s new unified smartwatch platform at MWC 2021 — sort of. Samsung did show off was a first look at what its new One UI Watch software will look like, and it elaborated on just what the new Google / Samsung partnership could mean for future Galaxy Watches. To be clear: what Samsung is showing of One UI Watch won’t be what all smartwatches built on the new unified Google / Samsung platform look like — it’s an added layer on top specifically for Samsung devices. The goal is a consistent look and experience across all of Samsung’s hardware and software, and so far it looks lovely. The Settings menu has been redesigned to look more like the phone’s menu, and things sync from the phone: if you have additional time zones set in your clock app, they’ll be there on the watch, and blocked callers on the phone will be blocked on watches, too. Samsung also showed off a new watchface design tool, which will be available for Android developers later this year to easily create new watchfaces for the platform. It’s unclear yet if current Tizen or Wear OS watchfaces will work with the new OS or One UI Watch, but the current options have also been seriously lacking, so any new choices — even ones largely reliant on developers — are welcome. Best of all, similar to the Apple Watch, when you install a smartwatch-compatible app on your phone, the corresponding watch app will automatically install on the watch as well. You won't need to manually install anything as you currently do on Tizen-based watches, or deal with the weird on-wrist app store that has made getting apps on Wear OS frustrating. You’ll just download an app to your phone and it should appear directly on your wrist, too. |



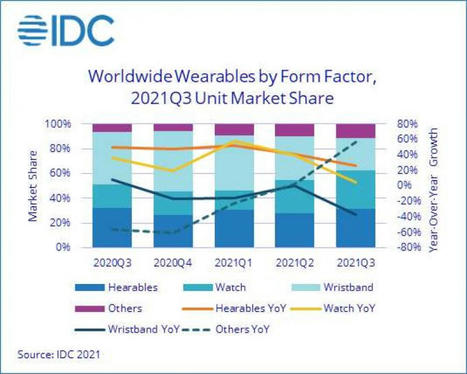


























IDC's report on the wearables market in Q3 of 2021 shows a near 10% increase over the same period last year. The growth was mainly down to hearables (headphones and earbuds), which grew 26.5% to capture nearly 65% of the market in Q3. Wrist-worn wearables followed with 34.7%. But according to IDC's numbers, demand is slowly shifting from wristbands to watches. Consumers are reportedly looking for more capable devices, and watches have gotten closer in price to bands. Apple held its number one spot, despite having to push the Watch Series 7 to Q4 due to supply issues. Its overall shares declined by 3.6%, but were kept solid by AirPods and Beats sales. Still, Apple grabbed over 53% of the dollar value for the entire market in Q3. Samsung tied Xiaomi for 2nd place with 12.7M shipments in Q3 - a 13.8% increase YoY. This is due to strong Galaxy Watch 4 sales. Xiaomi's market position worsened by nearly 24% over last year, due to its reliance on bands. Finally, Indian brand Imagine Marketing, which sells BoAt devices, found itself in the top 5, thanks to its strong marketing and affordable products.