Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
The evolutionary and ecological processes behind the origin of species are among the most fundamental problems in biology. In fact, many theoretical hypothesis on different type of speciation have been proposed. In particular, models of sympatric speciation leading to the formation of new species without geographical isolation, are based on the niche hypothesis: the diversification of the population is induced by the competition for a limited set of available resources. Interestingly, neutral models of evolution have shown that stochastic forces are sufficient to generate coexistence of different species. In this work, we put forward this dichotomy within the context of species formation, studying how neutral and niche forces contribute to sympatric speciation in a model ecosystem. In particular, we study the evolution of a population of individuals with asexual reproduction whose inherited characters or phenotypes are specified by both niche-based and neutral traits. We analyze the stationary state of the dynamics, and study the distribution of individuals in the whole phenotypic space. We show, both numerically and analytically, that there is a non-trivial coupling between neutral and niche forces induced by stochastic effects in the evolution of the population allowing the formation of clusters, that is, species in the phenotypic space. Remarkably, our framework can be generalized also to sexual reproduction or other type of population dynamics.
Via Samir
Kelp forests support diverse and productive ecological communities throughout temperate and arctic regions worldwide, providing numerous ecosystem services to humans. Literature suggests that kelp forests are increasingly threatened by a variety of human impacts, including climate change, overfishing, and direct harvest. We provide the first globally comprehensive analysis of kelp forest change over the past 50 y, identifying a high degree of variation in the magnitude and direction of change across the geographic range of kelps. These results suggest region-specific responses to global change, with local drivers playing an important role in driving patterns of kelp abundance. Increased monitoring aimed at understanding regional kelp forest dynamics is likely to prove most effective for the adaptive management of these important ecosystems.
|
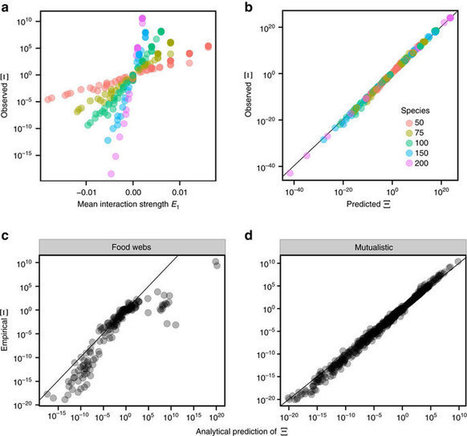
The role of species interactions in controlling the interplay between the stability of ecosystems and their biodiversity is still not well understood. The ability of ecological communities to recover after small perturbations of the species abundances (local asymptotic stability) has been well studied, whereas the likelihood of a community to persist when the conditions change (structural stability) has received much less attention. Our goal is to understand the effects of diversity, interaction strengths and ecological network structure on the volume of parameter space leading to feasible equilibria. We develop a geometrical framework to study the range of conditions necessary for feasible coexistence. We show that feasibility is determined by few quantities describing the interactions, yielding a nontrivial complexity–feasibility relationship. Analysing more than 100 empirical networks, we show that the range of coexistence conditions in mutualistic systems can be analytically predicted. Finally, we characterize the geometric shape of the feasibility domain, thereby identifying the direction of perturbations that are more likely to cause extinctions.
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...