With the explosive growth of online activity and social media around the world, the massive amount of real-time data created directly by populations of interest has become an increasingly attractive and fruitful source for analysis. Despite the limitation that social media users in the United States are not a random sample of the US population [7], there is a wealth of information in these data sets and uneven sampling can often be accommodated.
Indeed, online activity is now considered by many to be a promising data source for detecting health conditions [8, 9] and gathering public health information [10, 11], and within the last decade, researchers have constructed a range of public-health instruments with varying degrees of success.
Fine-tuning these algorithms is key to improving large-scale analysis of social media, whether the goal is to measure the caloric content of a tweet or to find the next developing news story. These technologies represent new ways of finding and understanding the conversations we're having as a country -- chatter that is increasingly moving online.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...








WHY THIS IS IMPORTANT
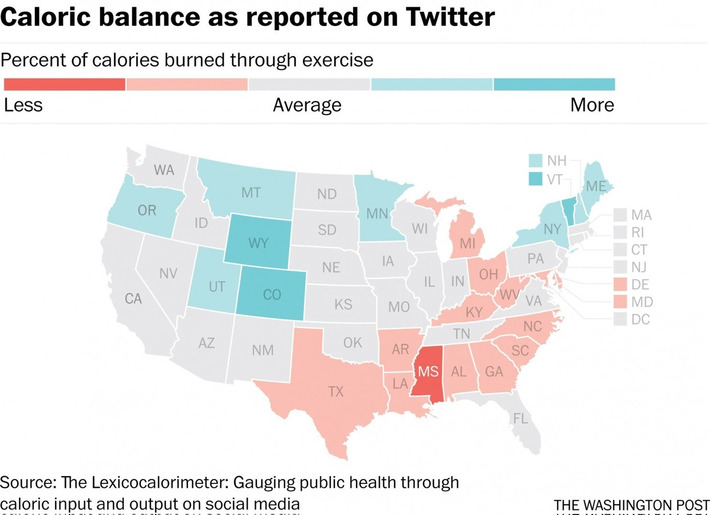
More insights on wellness and fitness from social media and big data. Here what is important to note is how we can extract knowledge from information that people share on social media. With more and more wearable devices and internet connected devices like refrigerators, cooktops, and water bottles, it is clear that more and more insight will be gathered from our digital exhaust.
More insights:
- more on the digital twin and digital exhaust: fmcs.digital/blog/digital-twin
- the website with all the data: panometer.org/instruments/lexicocalorimeter
- twitter can also help predict happiness: hedonometer.org/index.html
- the research paper: arxiv.org/pdf/1507.05098.pdf
- lapresse+ article (in french): plus.lapresse.ca/screens/d09ef280-9b06-4fe5-935c-4155336ef100%7C_0.html